Stunning Info About Does P2P Need A Router
O Que é P2P? Entenda Como Funciona A Rede P2P
P2P and Routers
1. Understanding the Basics
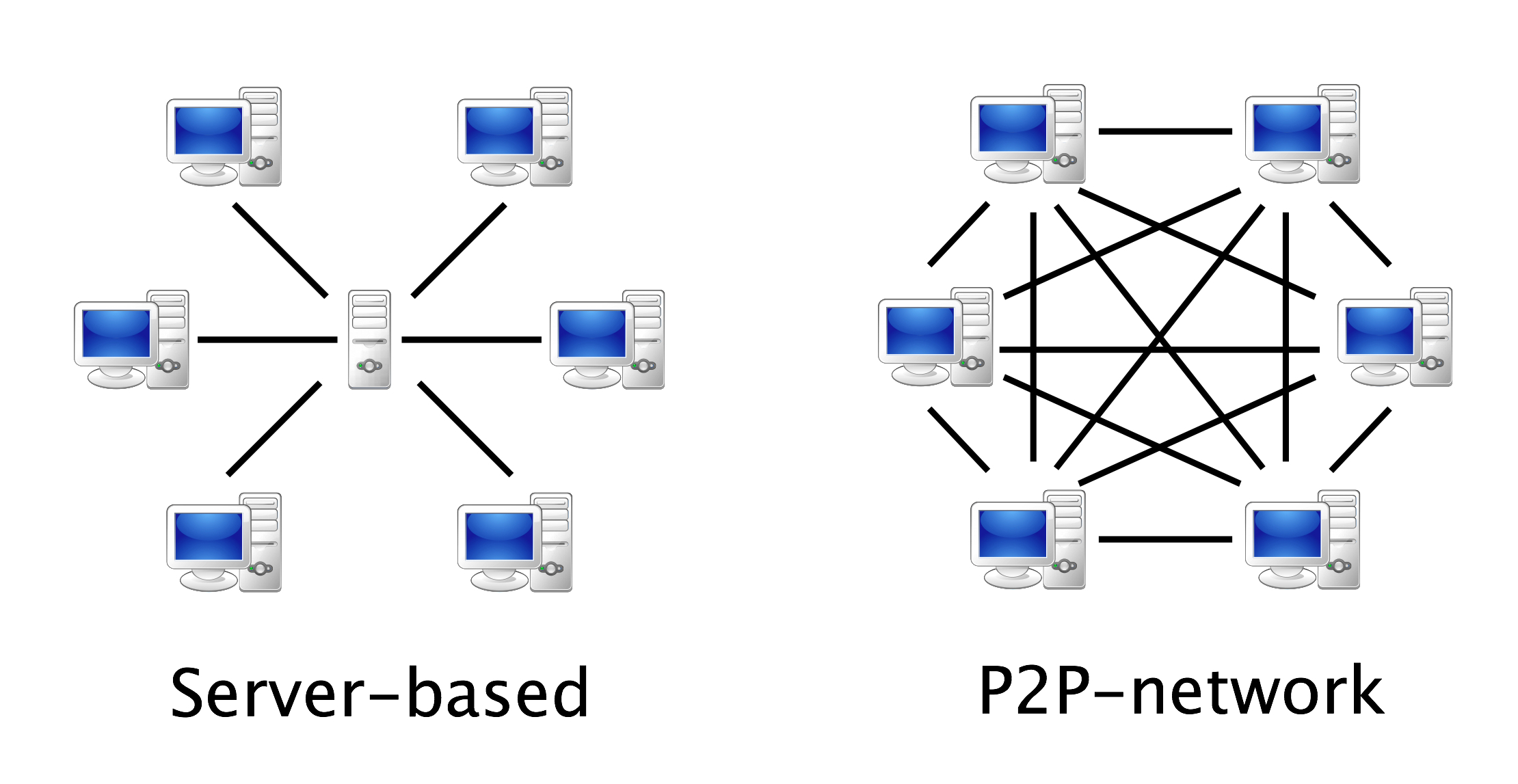
Let's dive right in! Peer-to-peer, or P2P, networking is like a digital potluck. Instead of relying on a central server to dish out the goods, each computer in the network shares files directly with others. Think of it as borrowing a cup of sugar from your neighbor instead of going to the supermarket — way more convenient (and potentially free!). This decentralized approach is what makes P2P networks so efficient and resilient.
Now, before you picture computers magically connecting across the globe with no help whatsoever, remember that even digital nomads need a home base of sorts. That's where the router comes in, playing a vital, if sometimes understated, role. It's the traffic controller, ensuring that data packets (those digital sugar cubes) reach their intended destinations.
Without a router, your devices wouldn't know how to communicate with each other, let alone the wider internet. It's like trying to send a letter without an address — the postman would have no clue where to deliver it! So, while P2P handles the file sharing aspect, the router is the unsung hero making that sharing possible.
Consider this: you want to share a funny cat video with a friend on a P2P network. Your computer needs to find your friend's computer. The router helps locate it within your local network. And if your friend is on a completely different network (perhaps on the other side of the world!), the internet, facilitated by routers all along the path, ensures that digital feline hilarity arrives safely.

What Is A PeertoPeer Network In Blockchain? CFTE
The Router's Role in P2P Networking
2. Navigating the Digital Highways
So, does P2P need a router? In almost every practical scenario, the answer is a resounding yes. Routers are essential for managing network traffic and ensuring that devices can communicate both within a local network (like your home) and with the wider internet. They're the gatekeepers, the interpreters, and the traffic cops all rolled into one unassuming box.
Imagine your home network as a small town. Each device (computer, phone, smart TV) is a house. The router is the post office and the network is the street. The router figures out which street each house is on. Without the router, you can't send something to a computer on your network.
Let's say you are downloading a torrent using a P2P client. Your router is handling the multiple connections that the P2P client is making to various peers. It's juggling all these data streams and making sure they get to the right place on your computer without causing chaos. It protects your devices by providing Network Address Translation (NAT) — presenting a single public IP address to the outside world while managing internal IP addresses for all your devices. This is crucial for security and prevents direct access to your devices from the internet.
A router also handles firewall duties. P2P can sometimes open security risks if not properly configured. So you want to make sure that your router is on point so you aren't compromised when torrenting.

Reactive Android Development Ppt Download
NAT and Port Forwarding
3. Unlocking the Potential
Now, here's where things get a bit technical but bear with me. NAT, or Network Address Translation, is a technique routers use to allow multiple devices on a private network to share a single public IP address. It's like a company using a single switchboard number for all its employees. Everyone calls the main number, and then the operator (the router) directs the call (the data) to the right person (the device).
This is generally a good thing for security, as it hides your internal network structure from the outside world. However, NAT can sometimes interfere with P2P networking. Why? Because some P2P applications rely on direct connections between peers. NAT can block these connections, making it difficult for your computer to be "found" by other peers on the network.
Enter port forwarding! Port forwarding is like telling the switchboard operator (the router) to always direct calls (data) coming in on a specific extension (port) to a particular person (device). By configuring port forwarding on your router, you can allow specific P2P traffic to bypass NAT and reach your computer directly. This can significantly improve P2P performance and download speeds.
While port forwarding can be helpful, it's essential to use it cautiously. Opening ports can potentially increase your security risk, so only forward ports for applications you trust and understand. Think of it as only giving out your direct line to people you really trust! Be responsible. And always, always keep your router's firmware up to date!
Troubleshooting P2P and Router Issues
4. When Things Go Wrong
Sometimes, even with the best router and careful configuration, P2P networking can run into snags. Maybe your download speeds are slow, or you can't connect to certain peers. Don't panic! A few simple troubleshooting steps can often resolve the issue. First, double-check your firewall settings. Make sure your P2P application isn't being blocked by your firewall or antivirus software. Firewalls will sometimes be a roadblock, no matter how big you are.
Next, ensure your router's firmware is up to date. Outdated firmware can contain bugs that affect P2P performance. Regularly updating your router's firmware is like giving it a regular checkup to make sure everything is running smoothly. Then, try power cycling your router. This is the digital equivalent of giving it a good smack (gently, of course!). Simply unplug the router, wait 30 seconds, and plug it back in. This can often clear up temporary glitches and refresh the connection.
If you're still having problems, check your P2P application's settings. Make sure you're using the correct port numbers and that your connection settings are optimized for your network. If you've been messing with things, restore the defaults. Also, be mindful of your internet service provider's policies. Some ISPs may throttle or block P2P traffic. If you suspect this is the case, try using a VPN to encrypt your traffic and bypass any restrictions.
Finally, if all else fails, consult your router's manual or the online documentation for your P2P application. There may be specific troubleshooting steps or configuration tips that can help you resolve the issue. And don't be afraid to seek help from online forums or communities — chances are someone else has encountered the same problem and found a solution!

What Is A P2P Network? YouTube
Alternatives to Traditional Routers for P2P
5. Exploring Options
While a traditional router is the most common setup for most homes, there are some alternatives to consider, particularly if you're a heavy P2P user or have more advanced networking needs. Mesh Wi-Fi systems are becoming increasingly popular, offering wider coverage and more reliable connections than traditional routers. These systems use multiple nodes to create a unified network, eliminating dead zones and improving overall performance.
Another option is to use a router with advanced features specifically designed for P2P networking. Some routers offer built-in VPN support, QoS (Quality of Service) settings, and other features that can optimize P2P traffic and improve security. These routers often come with more robust firewalls and intrusion detection systems, providing enhanced protection against potential threats.
And then there's the option of using a dedicated server for P2P networking. This involves setting up a separate computer to handle all your P2P traffic. This can be particularly useful if you're running a large-scale P2P network or want to isolate your P2P activity from your main computer. However, this option requires more technical expertise and can be more expensive than using a traditional router.
Finally, for those who are technically inclined, there's the option of building your own router using open-source software like pfSense or OpenWRT. This gives you complete control over your network configuration and allows you to customize it to your specific needs. However, this option requires a significant amount of technical knowledge and can be quite complex to set up.
What’s The Difference Between Peertopeer (P2P) Networks And Client
FAQ
6. Your Questions Answered
Let's address some common questions about P2P and routers:
Q: Does using P2P slow down my internet speed for everyone else in the house?
A: It can, especially if you're downloading or uploading large files. P2P can consume a significant amount of bandwidth, potentially impacting the internet experience for other users. Using Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router can help prioritize certain types of traffic (like video streaming or online gaming) over P2P traffic to minimize the impact on other users.
Q: Is it safe to use P2P networks?
A: It can be risky. P2P networks can be a breeding ground for malware and viruses. It's important to use reputable P2P applications, keep your antivirus software up to date, and be cautious about downloading files from unknown sources. Using a VPN can also help protect your privacy and security on P2P networks.
Q: My P2P downloads are really slow. What can I do?
A: There are several things you can try. First, make sure your firewall isn't blocking your P2P application. Next, configure port forwarding on your router. Also, try increasing the number of connections allowed in your P2P application. Finally, check your internet connection speed and make sure you're not being throttled by your ISP.