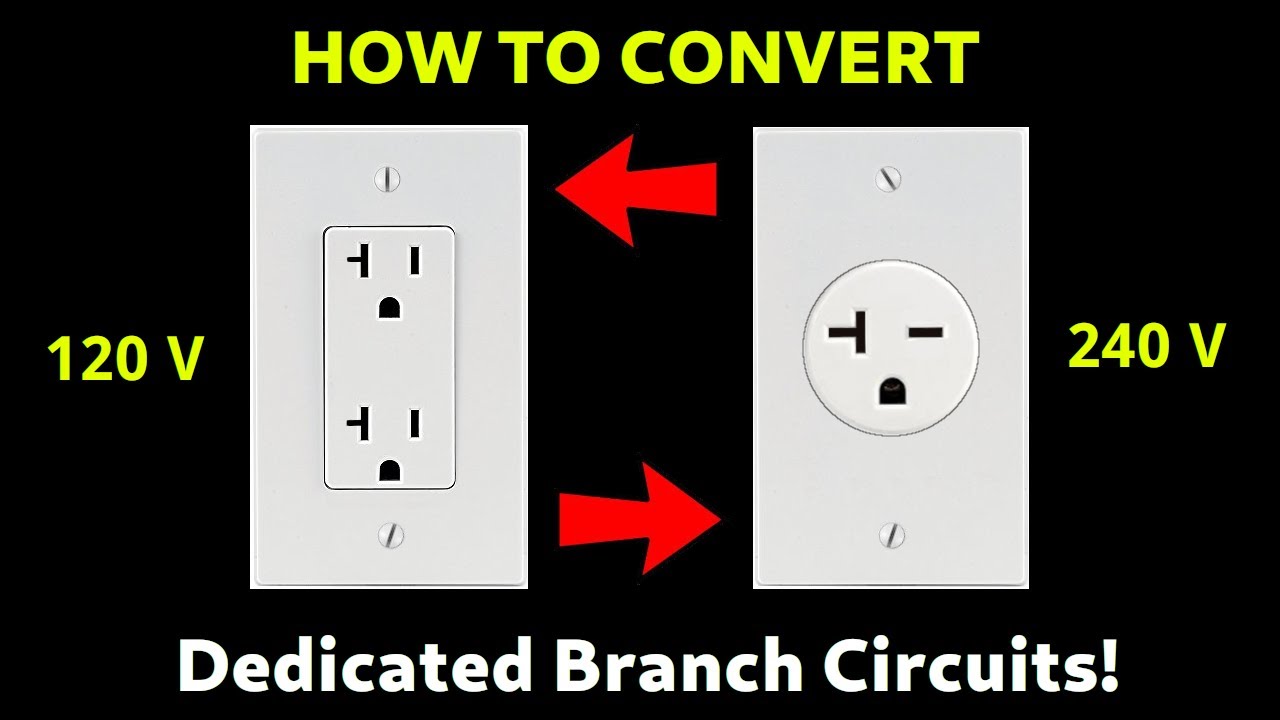
Cool Info About Is 240 The Same As 220V

Decoding the Voltage Mystery
1. Understanding Voltage Basics
Ever wondered if the electricity powering your gadgets is always exactly what it says on the tin? You see "220V" plastered on appliances, and then you hear whispers of "240V." Are they the same? Are we living on the edge of a voltage cliff? Let's break down this electrifying enigma (pun intended!).
Think of voltage like water pressure in pipes. A higher voltage is like more water pressure pushing through the wires. Different countries and regions have standardized on different voltage levels for their electrical grids. This standardization aims to ensure appliances function correctly and, most importantly, safely.
But here's a little secret: the voltage isn't always a rock-solid, unyielding number. There's a bit of wiggle room, a tolerance if you will. It's like saying "around 70 degrees" when talking about the weather; it might be 68, it might be 72, but it's generally in that ballpark. In the electrical world, this tolerance means the actual voltage can fluctuate a bit.
So, while you might see 220V on a label, the power company could be sending 230V or even 240V through the lines. It's all within a pre-defined range, designed to keep things running smoothly (and prevent your toaster from staging a revolt).
The "Close Enough" Factor
2. Why the Variance?
Okay, so why isn't the voltage exactly 220V all the time? Well, a number of factors can contribute to these minor fluctuations. Things like the load on the power grid (how much electricity everyone is using), the distance from the power plant, and even the time of day can have an impact. Imagine rush hour on an electrical highway — things get a little congested!
Also, electrical equipment is designed with a certain tolerance in mind. They aren't built to explode if the voltage is a single volt off! Manufacturers understand that real-world conditions aren't always perfect, so they design their products to handle a range of voltages. It's all about robust design and reliability.
Think of it like your car's speedometer. It probably isn't exactly accurate all the time. There's a bit of leeway. Similarly, electrical appliances are built to handle these small variations in voltage without any issues.
The important point is that these fluctuations are usually within acceptable limits. Power companies have regulations and monitoring systems in place to keep the voltage within a safe and functional range. So, while the voltage might not be a perfect 220V at every single moment, it's generally close enough to keep your devices happy and humming along.
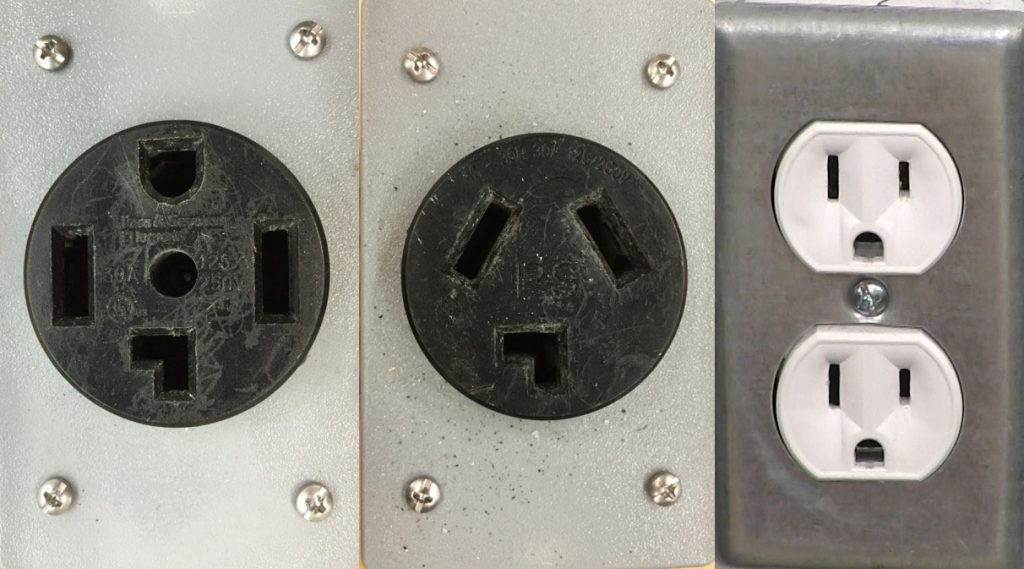

Difference Between 220 Volt And 240
Regional Differences
3. Voltage Standards Around the World
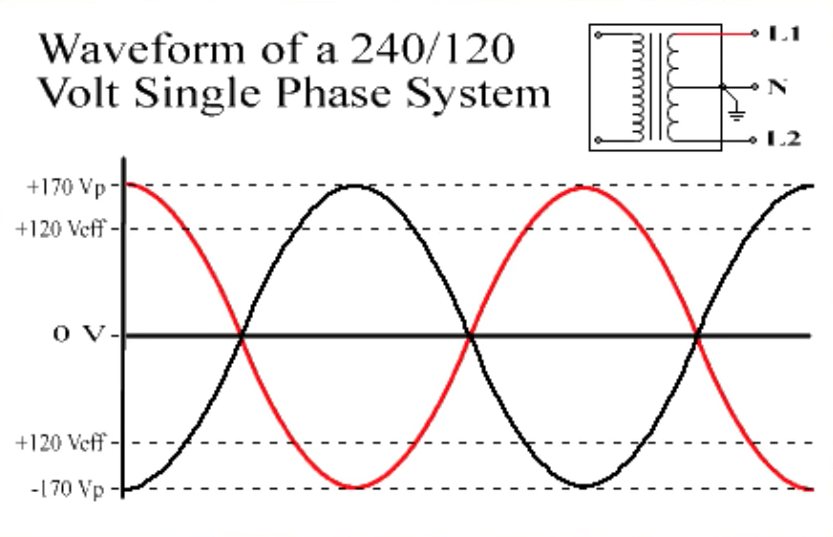
Did you know that the world doesn't agree on a single voltage standard? It's true! North America primarily uses 120V, while many other parts of the world, including Europe, Asia, and Africa, use 220V-240V. It's a bit like driving on different sides of the road — you just need to know the rules of the local electrical grid!
This difference in voltage standards stems from historical reasons and the way electrical grids were initially developed. Early electrical systems in the US used 110V (which later evolved to 120V), while Europe opted for higher voltages. There's no inherent "better" voltage; both systems have their advantages and disadvantages.
If you're a frequent traveler, this is crucial information! Plugging a 120V appliance into a 240V outlet (without a proper adapter or converter) is a recipe for disaster — think sparks, smoke, and potentially a very unhappy appliance. Always check the voltage requirements of your devices and use the appropriate adapter or converter when traveling internationally.
Think of it as a lesson learned from experience. Each region chose its voltage, built its infrastructure, and now it is difficult and expensive to change, so we are stuck with regional differences. Always be sure to double-check appliance and outlet voltage when traveling.
Is 208v 230v And 240v Same
Safety First
4. Knowing the Limits
While minor voltage fluctuations are generally harmless, there are situations where you should be concerned. If you notice frequent voltage dips or surges (lights flickering, appliances behaving erratically), it could indicate a problem with your electrical system or the power grid. This is where a qualified electrician comes in handy.
Extreme voltage fluctuations can damage your appliances or even pose a fire hazard. If you suspect a problem, it's always best to err on the side of caution and consult with a professional. They can diagnose the issue and recommend appropriate solutions, such as installing a surge protector or voltage regulator.
Also, be aware of the voltage requirements of your appliances, especially high-power devices like air conditioners or electric heaters. Using an appliance that's not designed for the voltage in your home can be dangerous and could void the warranty. Always double-check the label before plugging it in!
Remember, electricity is a powerful force, and it's important to treat it with respect. If you're ever unsure about something, don't hesitate to seek professional help. A little bit of knowledge and caution can go a long way in ensuring your safety and protecting your valuable electronics.

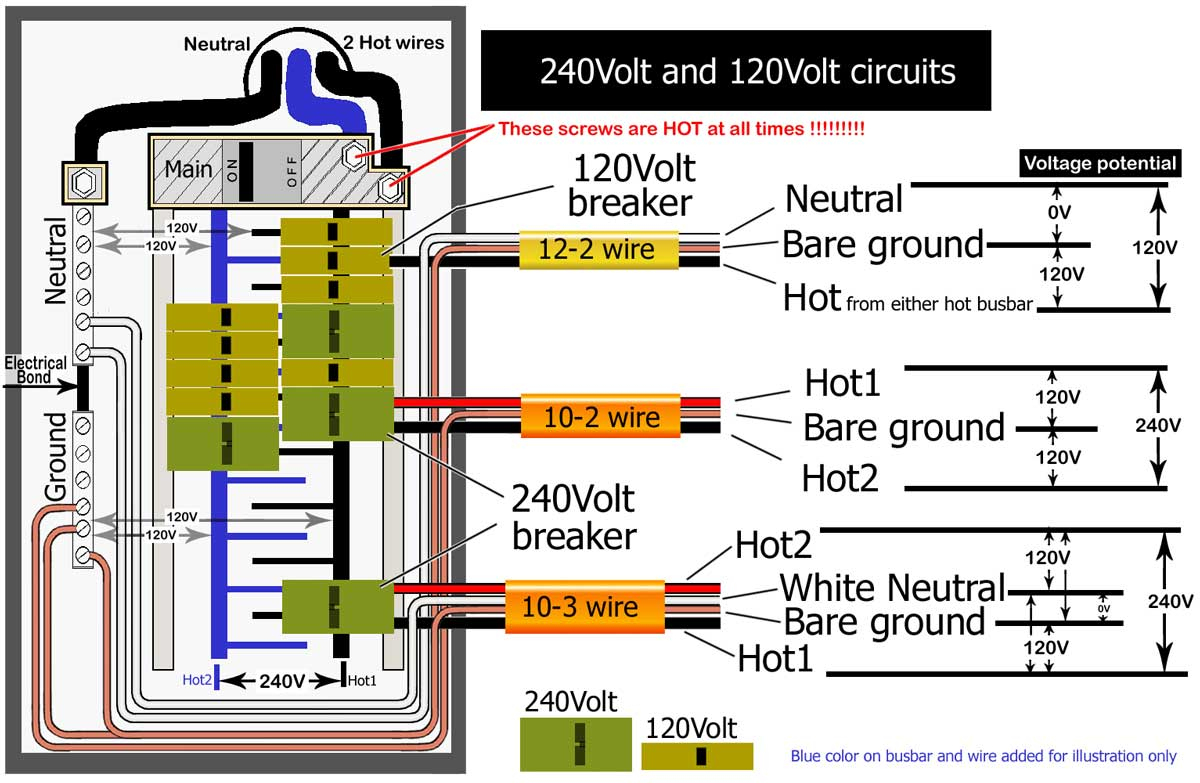
So, Are They the Same? The Verdict
5. Drawing the Line
So, circling back to our original question: is 240V the same as 220V? The simple answer is: essentially, yes. They are often used interchangeably because 220V often represents the nominal voltage, while 240V falls within the acceptable tolerance range. Think of it as the difference between saying "it's about five o'clock" and knowing the precise minute.
In practical terms, most appliances designed for 220V will function perfectly well on a 240V supply. However, it's always a good idea to check the manufacturer's specifications to be sure. Some sensitive electronic equipment may require a more stable voltage, in which case a voltage regulator might be a wise investment.
The electrical grid is a complex system, and voltage isn't always a fixed number. There's a bit of wiggle room, a tolerance that allows for minor fluctuations. As long as the voltage stays within the acceptable range, your appliances should be safe and happy. So, next time you hear someone mention 240V when you're expecting 220V, don't panic! It's probably just business as usual on the electrical highway.
The important takeaway is that you should research the product requirements, especially for expensive appliances that you want to use for a longer period. Having a safe house is a comfortable house.
Who Else Wants Info About Is 120 A High Voltage Alternativeresult29
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Your Voltage Questions Answered
Q: Will my 220V appliance explode if I plug it into a 240V outlet?A: Probably not. Most 220V appliances are designed to handle a range of voltages, typically including 240V. However, it's always best to check the appliance's label or manual to be sure.
Q: I see my lights flicker sometimes. Is that a voltage problem?A: It could be. Light flickering can be a sign of voltage fluctuations. If it happens frequently or is accompanied by other electrical issues, consult a qualified electrician.
Q: What is a voltage regulator, and do I need one?A: A voltage regulator is a device that stabilizes the voltage supply to your appliances. They are often used to protect sensitive electronic equipment from voltage fluctuations. You might need one if you live in an area with unreliable power or if you have expensive electronics that are particularly sensitive to voltage changes.
Q: Can I use a US 120V appliance in Europe with just an adapter?A: No, not usually. You'll need a voltage converter in addition to an adapter. An adapter simply changes the shape of the plug to fit the outlet, but it doesn't change the voltage. Using a 120V appliance on a 240V system without a converter can damage the appliance.